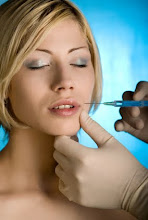
Botox is a drug made from a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It's the same toxin that causes a life-threatening type of food poisoning called botulism. Botox injections work by weakening or paralyzing certain muscles or by blocking certain nerves. The effects last about three to four months. Side effects can include pain at the injection site, flu-like symptoms, headache and upset stomach. Injections in the face may also cause temporary drooping eyelids.
In large amounts, this toxin can cause botulism which you probably associate with food poisoning. Despite the fact that one of the most serious complications of botulism is paralysis, scientists have discovered a way to use it to human advantage. Small, diluted amounts can be directly injected into specific muscles causing controlled weakening of the muscles.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved such usage in the late 1980s upon the discovery that Botox could stop ailments like blepharospasm (uncontrolled blinking) and strabismus (lazy eye). Cosmetic physicians have been using Botox for years to successfully treat wrinkles and facial creases. In April 2002, Botox gained FDA approval for treatment of moderate to severe frown lines between the eyebrows called glabellar lines. However, Botox is often used for other areas of the face as well.
0 comments:
Post a Comment